Periodontal (Gum) Treatments
|
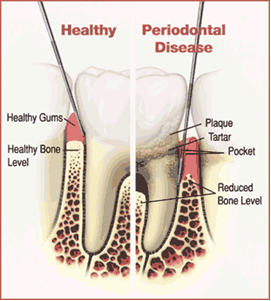
Gum disease is an infection in the tissues that support your teeth including the gums and jaw bone. If bacteria accumulates below the gum line, it will release toxins that cause gum inflammation, bleeding, bad breath, bone loss, and loose teeth.
Gum diseases progress in two stages. The first stage is GINGIVITIS, which is a milder and reversible form of periodontal disease. If Gingivitis is left untreated, it may progress to a more serious form gum disease called PERIODONTITIS. Periodontitis not only affects the gums but also causes destruction of the bone surrounding your teeth. This will cause your tooth to become loose and may eventually need to be removed. |
Scaling and Root Planning
|
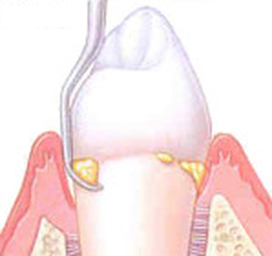
Scaling and Root Planning are procedures used to treat periodontal diseases. Scaling involves using special instruments to remove plaque and calculus (tartar) that has accumulated on the tooth surfaces. Scaling alone will not always remove the bacterial deposits that are embedded in the rough surfaces of the root of your teeth. Root Planning is a procedure in which the rough surfaces of the tooth root are removed in order to create a smooth, hard and clean surfaces.
About 1-2 weeks after removal of bacteria that causes gum disease, the tissues should begin to heal, the redness should disappear, and the gums should no longer bleed. It will be very important for the patient to maintain excellent oral hygiene in order to prevent the gum disease from recurring. If gum disease persists even after Scaling and Root Planning, more advanced procedures may need to be performed. In this case, we would refer you to a Periodontist, who is a specialist in treating more advanced cases of periodontal disease. |